Blockchain Forks: Hard Forks vs Soft Forks
Blockchain forks are fundamental to the evolution of decentralized networks, acting as turning points for upgrading protocols or resolving conflicts. Forks occur when a blockchain network splits into two, resulting from changes in the underlying code. However, not all forks are the same; they are generally divided into two categories: hard forks and soft forks. In this blog, we will explore both types, their differences, and their impacts on blockchain ecosystems.
1. What is a Blockchain Fork?
A blockchain fork happens when participants on a blockchain network no longer follow the same rules, creating a divergence in the blockchain’s path. This can be a planned update to improve security, scalability, or functionality, or an unplanned split caused by disagreements among developers and community members. The two primary types of forks are hard forks and soft forks.
2. What is a Hard Fork?
A hard fork is a radical change to the blockchain protocol, rendering previously invalid blocks or transactions valid (or vice versa). Since this type of fork is not backward-compatible, all network participants must upgrade to the new version to stay on the same network. Those who do not update continue on the old version, resulting in two separate blockchains.
Examples of Hard Forks:
- Bitcoin Cash (BCH): Created from Bitcoin to improve scalability by increasing block size.
- Ethereum Classic (ETC): Formed from Ethereum after disagreements over reversing a transaction related to the DAO hack.
Impact of Hard Forks:
- New Chain Creation: A hard fork can split the blockchain into two networks with different features.
- Disrupts Consensus: All participants must align with the new rules to remain on the primary network.
- Potential Coin Distribution: Forked chains often result in new cryptocurrencies for holders of the original coin.
3. What is a Soft Fork?
A soft fork is a backward-compatible change to the blockchain protocol. With a soft fork, only previously valid blocks or transactions are made invalid, and nodes that do not upgrade can still participate in the network. This ensures that the blockchain remains unified, without splitting into separate chains.
Examples of Soft Forks:
- SegWit (Segregated Witness): A Bitcoin soft fork introduced to increase block capacity by removing certain transaction data from blocks.
- Taproot: Another Bitcoin soft fork aimed at improving privacy and transaction efficiency.
Impact of Soft Forks:
- Maintains Single Chain: No new blockchain or cryptocurrency is created.
- Optional Upgrades: Participants can choose to upgrade, but the older version remains compatible.
- Lower Risk of Disruption: Fewer conflicts arise since the changes are minor and backward-compatible.
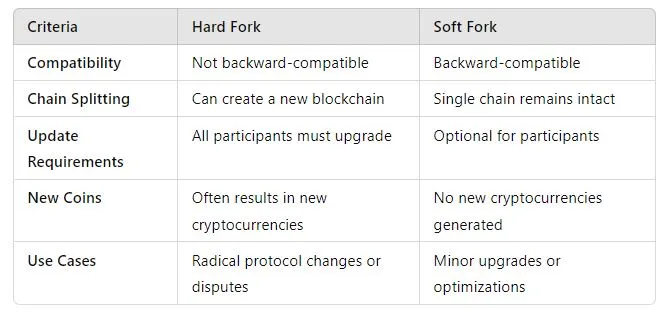
4. Hard Forks vs. Soft Forks: Key Differences
5. Why Forks Matter in Blockchain Evolution
Forks enable blockchains to evolve and adapt to changing needs. Hard forks provide room for innovation or ideological differences, creating new networks that offer distinct use cases. On the other hand, soft forks ensure smoother, incremental upgrades that maintain network integrity without disruptions.
Both types of forks play a critical role in blockchain governance by allowing stakeholders to propose and implement changes. As blockchains grow, forks empower communities to decide which path aligns with their values and priorities, driving the decentralized economy forward.
6. Conclusion
Understanding blockchain forks — especially the differences between hard forks and soft forks — is crucial for anyone engaging in decentralized networks. Hard forks offer opportunities for radical innovation but come with the risk of network fragmentation, while soft forks provide a safer path for gradual upgrades. Both types are essential for blockchain growth and demonstrate the dynamic, ever-evolving nature of decentralized technology.
At DeBlockX, we stay at the forefront of blockchain innovation, navigating forks and protocol upgrades to create products that leverage the best of Web3. Stay tuned with us for more insights into blockchain evolution!
Copyright © 2024 DeBlockX
All Rights Reserved